B. Inorganic sulfur metabolism of green sulfur bacteria
- H. Sakurai, T. Ogawa, M. Shiga and K. Inoue (2010) Inorganic sulfur oxidizing system in green sulfur bacteria.Photosynthesis Research. 104: 163-176
- T. Ogawa, T. Furusawa, M. Shiga, D. Seo, H. Sakurai and K. Inoue (2010) Biochemical studies of the soxF-encoded monomeric flavoprotein purified from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobaculum tepidum that stimulates in vitro thiosulfate oxidation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74: 771-780
- T. Ogawa, T. Furusawa, R. Nomura, D. Seo, N. H. Matsuda, H. Sakurai, K. Inoue (2008) SoxAX binding protein, a novel component of the thiosulfate-oxidizing multienzyme system in the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum, J. Bacteriol.190: 6097-6110
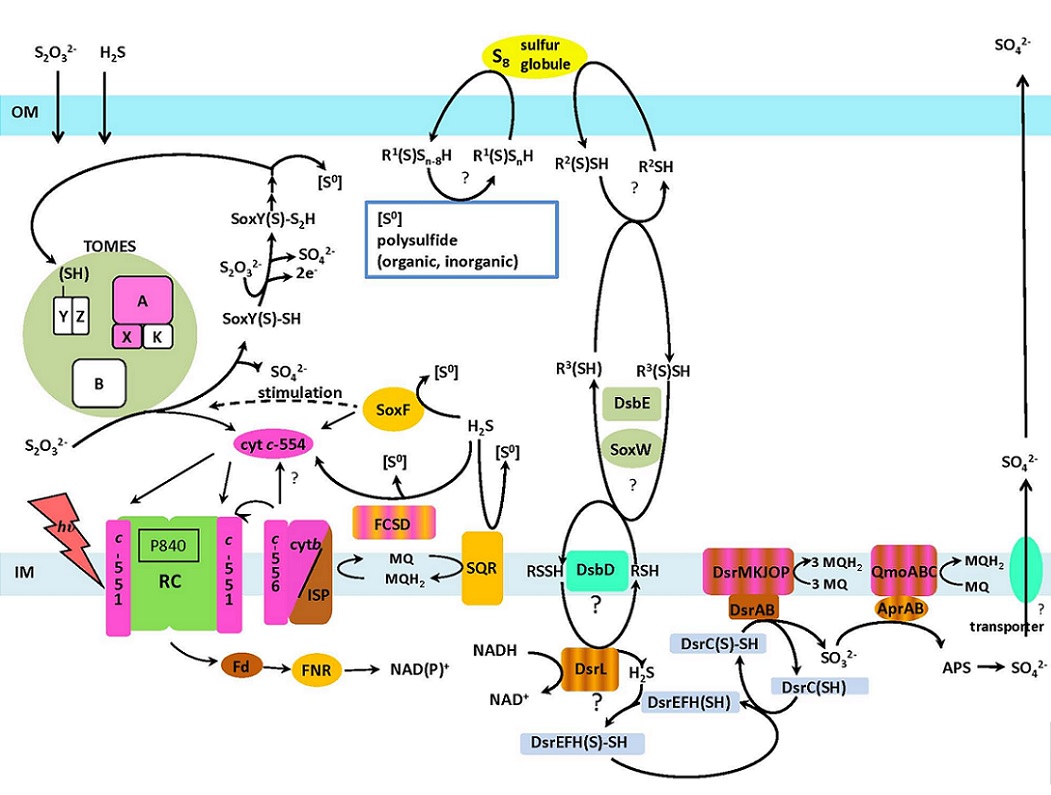
Overview of known and hypothesized pathways of electronand inorganic sulfur compounds in Chlorobaculum tepidum.
Thin arrows indicate pathways of e-, and thick ones, metabolic or transport pathways of substrates/products. ? hypothetical, Apr adenosine 50-phosphosulfate reductase, APS adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate, c cytochrome c with thewavelength (nm) of the a-band of the reduced form, cyt b/ISP cyt b/Rieske-type ISP complex, Dsb homologues encoded by genes in thedsb gene cluster encoding thiol:disulfide interchange proteins, Dsrproteins encoded by genes in the dsr gene cluster encoding dissimilatory sulfite reductase proteins, FCSD flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase, Fd ferredoxin, FNR ferrodoxin-NAD(P)?/NAD(P)H oxidoreductase, IM inner membrane, MQ menaquinone, OM outer membrane, Qmo quinone oxidizing membrane protein, R1,2,3 hypothetical thiol, RC reaction center, [S0] the zero-valence sulfur or the equivalent (sulfur atom in organic and inorganic polysulfide, elemental sulfur), Sox proteins encoded by genes in the sox gene cluster, SQR sulfide-quinone reductase, TOMES thiosulfate oxidizing multi-enzyme system.
(adapted from Sakurai et al. (2010) Photosynthesis Res. 104:163–176
C. Electron transport pathway of green sulfur bacteria
- D. Seo, K. Kamino, K. Inoue, H. Sakurai (2004) Purification and characterization of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase encoded by Bacillus subtilis yumC. Arch. Microbiol. 182: 80-89
- D. Seo, H. Sakurai (2002) Purification and characterization of ferredoxin-NAD(P)+ reductase from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1597: 123-132